vol. 36, No. 8, 2025
This special issue of the Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society highlights the growing role of machine learning in chemistry, showcasing its impact on accelerating discoveries, predicting molecular properties, and analyzing complex datasets across various sub-fields. The integration of artificial intelligence is reshaping research approaches and pushing the boundaries of chemical science. The published articles cover a wide range of topics-from the refinement of density functionals in strongly correlated systems to applications in medicinal chemistry, materials design, and the development of FAIR data strategies-demonstrating the versatility and transformative potential of machine learning in the chemical sciences.
Special Issue Machine Learning
Editorial J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250106, 1
Embracing the Machine Learning Revolution in Chemistry
Mauricio D. Coutinho-Neto  ; Paula Homem-de-Mello
; Paula Homem-de-Mello
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250106
Review J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250067, 1-13
Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing in Chemistry and Materials Science
How to cite this article

This work paper the applications of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) in chemistry and materials science, highlighting their role in chemical entity recognition, reaction prediction, materials discovery, and literature analysis.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250067
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250082, 1-20
A Survey of Basic Concepts and Applications of Machine Learning to Chemistry
Julio Cesar Duarte  ; Antonio G. S. de Oliveira-Filho
; Antonio G. S. de Oliveira-Filho  ; Matheus Máximo-Canadas
; Matheus Máximo-Canadas  ; Rubens C. Souza
; Rubens C. Souza  ; Itamar Borges Jr.
; Itamar Borges Jr.

Machine learning uses algorithms and statistical models for defined tasks and learning patterns from data without explicit instructions. Its basic concepts and some applications are reviewed.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250082
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250084, 1-17
Determination of Thermal Process Kinetics by Artificial Neural Networks: A Review Considering Isothermal and Non-Isothermal TG and DSC Data
Rita C. O. Sebastião  ; Natália R. S. Araujo
; Natália R. S. Araujo  ; Felipe S. Carvalho
; Felipe S. Carvalho  ; Bárbara D. L. Ferreira
; Bárbara D. L. Ferreira  ; João Pedro Braga
; João Pedro Braga

Kinetic of thermal processes can be accurately determined by combining artificial neural network with thermal analysis techniques.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250084
Full Paper J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250004, 1-8
Computational Modeling and Biological Evaluation of Benzophenone Derivatives as Antileishmanial Agents
Bárbara F. Farias  ; Miller S. Ferreira
; Miller S. Ferreira  ; Daniel O. Miranda
; Daniel O. Miranda  ; Tayná R. Nunes; Natália F. Pereira; Patrícia F. Espuri
; Tayná R. Nunes; Natália F. Pereira; Patrícia F. Espuri  ;
;
Jaqueline P. Januario  ; Fábio A. Colombo
; Fábio A. Colombo  ; Marcos J. Marques
; Marcos J. Marques  ; João L. B. Zanin
; João L. B. Zanin  ; Marisi G. Soares
; Marisi G. Soares  ; Thiago B. de Souza
; Thiago B. de Souza  ; Diogo T. Carvalho
; Diogo T. Carvalho  ; Daniela A. Chagas-Paula
; Daniela A. Chagas-Paula  ; Danielle F. Dias
; Danielle F. Dias 

Application of machine learning and computational tools to predict antileishmanial activity, emphasizing the synergy of computational and experimental methods in developing novel therapeutic agents.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250004
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-2025001, 1-14
Computational Investigations on Inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Shikimate Kinase: Machine Learning, Docking, Molecular Dynamics and Free Energy Calculations
Anderson J. A. B. dos Santos; Paulo A. Netz

Machine learning combined with virtual screening has enabled the discovery of a significant variety of molecules exhibiting high affinity with shikimate kinase. Subsequent evaluation through molecular dynamics and free energy calculations has facilitated the identification of potential inhibitor candidates.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250016
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250022, 1-10
Deep Reinforcement Learning and Structure-Based Approaches in the de novo Design of a New Potential Inhibitor of F13 Protein from Monkeypox Virus
Edilson B. Alencar Filho  ; Rosalvo F. Oliveira Neto; Vanessa C. Santos; Allysson L. S. Ferreira
; Rosalvo F. Oliveira Neto; Vanessa C. Santos; Allysson L. S. Ferreira

De novo design of a new lead compound with potential inhibitory effect on monkeypox virus F13 protein (VP37) by deep reinforcement learning and structure-based drug design.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250022
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250028, 1-11
Drug Repurposing for Trypanosomiasis: Using Machine Learning Models and Polypharmacology to Identify Multitarget Candidates
Karime Zeraik A. Domingues; Alexandre de F. Cobre; Mariana M. Fachi; Raul Edison L. Lazo; Luana M. Ferreira;
Roberto Pontarolo

This study utilizes Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR)-based machine learning models, validated with bioactivity data median inhibitory concentration (IC50) of compounds against Trypanosoma brucei and Trypanosoma cruzi, for screening Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved compounds as candidates for repurposing in the treatment of both trypanosomiases.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250028
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250029, 1-12
Discrimination between COVID-19 Positive and Negative Blood Sera Using an Unmodified Disposable Impedimetric Sensor and Multivariate Analysis
Ingrid G. B. L. Cruz; Flávia R. P. Sales; Wallace D. Fragoso  ; Lúcio R. C. Castellano; Fabyan E. L. Beltrão; Talita N. Cardoso;
; Lúcio R. C. Castellano; Fabyan E. L. Beltrão; Talita N. Cardoso;
Maísa S. de Oliveira; Sherlan G. Lemos

The blood composition imbalance following coronavirus disease (COVID-19) causes a systematic change in impedance, which can be modelled by multivariate analysis.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250029
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250037, 1-12
Machine Learning Prediction of the Most Intense Peak of the Absorption Spectra of Organic Molecules
Rubens C. Souza  ; Julio C. Duarte
; Julio C. Duarte  ; Ronaldo R. Goldschmidt
; Ronaldo R. Goldschmidt  ; Itamar Borges Jr.
; Itamar Borges Jr.

Molecules from the QM-symex database are converted to SMILES (simplified molecular input line entry system) and stored in a new QM-symex-modif dataset with their target properties. The data is processed and used in machine learning models to develop predictive models for photophysical properties.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250037
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250043, 1-9
Machine Learning to Treat Data for the Design and Improvement of Electrochemical Sensors: Application for a Cancer Biomarker
Gisela Ibáñez Redín; Daniel C. Braz; Débora Gonçalves; Osvaldo N. Oliveira Jr.
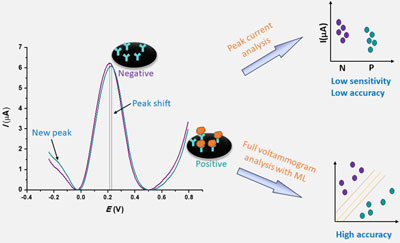
Full voltammogram analysis through machine learning for enhanced detection in electrochemical immunosensors.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250043
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250050, 1-10
Assessing Emissions of Biogenic Volatile Organic Compounds and Their Correlation with Abiotic Factors in an Atlantic Forest Reserve Using Supervised Learning Methods
Ana Paula S. Figueiredo; Junio R. Botelho; Marcia Helena C. Nascimento  ; Maria Cristina Canela
; Maria Cristina Canela  ; Royston Goodacre;
; Royston Goodacre;
Paulo R. Filgueiras; Murilo O. Souza

This study employs supervised learning methods, including Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) with bootstrap resampling and Support Vector Machine (SVM) ensemble, to analyze biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs) emissions in the Atlantic Forest, achieving high classification accuracy.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250050
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250054, 1-9
Quantum Active Learning for Structural Determination of Doped Nanoparticles - A Case Study of 4Al@Si11
Maicon Pierre Lourenço  ; Mosayeb Naseri; Lizandra Barrios Herrera; Hadi Zadeh-Haghighi
; Mosayeb Naseri; Lizandra Barrios Herrera; Hadi Zadeh-Haghighi  ; Daya Gaur; Christoph Simon;
; Daya Gaur; Christoph Simon;
Dennis R. Salahub

A quantum active learning method (QAL) for automatic structural determination of doped materials has been developed and implemented in the QMLMaterial software. QAL uses quantum circuits for data encoding to create quantum machine learning models on-the-fly.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250054
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250063, 1-9
QSAR-Lit: A No-Code Platform for Predictive QSAR Model Development - From Data Curation to Virtual Screening
Igor H. Sanches; Francisco L. Feitosa; Jade M. Lemos; Sabrina Silva-Mendonça; Ester Souza; Victoria F. Cabral; José T. Moreira-Filho; Henric Gil; Bruno J. Neves; Rodolpho C. Braga; Joyce V. V. B. Borba; Carolina H. Andrade

The figure illustrates the core components of quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR)-Lit, a platform designed to streamline the QSAR modeling process. It encompasses data curation, descriptor calculation, machine learning, and virtual screening, enabling seamless and efficient analysis for drug discovery applications.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250063
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250070, 1-18
Machine Learning Models for the Identification of Natural Products with Anti-Schistosomiasis Activity
Rafaela M. de Angelo; Vinícius G. Maltarollo; João Henrique G. Lago; Kathia Maria Honorio

Machine learning models were used to predict the biological activity of natural products against Schistosoma mansoni. Virtual screening identified 14 promising compounds, which were further analyzed for absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADMET) properties.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250070
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250071, 1-13
How Could Perform a Predictive Model Created Using the Heterogeneous Chemical Space of Compounds against Trypanosoma cruzi?
João L. Baldim  ; Welton Rosa; Thais A. C. Silva; Daiane D. Ferreira; Andre Gustavo Tempone; Daniela Aparecida C. de Paula
; Welton Rosa; Thais A. C. Silva; Daiane D. Ferreira; Andre Gustavo Tempone; Daniela Aparecida C. de Paula  ; Marisi G. Soares; João Henrique G. Lago
; Marisi G. Soares; João Henrique G. Lago

From chemical compounds to predicting the antitrypanosomal activity of new candidates against Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250071
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250090, 1-15
Predicting Glycerol Electrochemical Oxidation Potentials Using Machine Learning
João M. L. Soares  ; Theodora W. von Zuben
; Theodora W. von Zuben  ; Airton G. Salles Jr.
; Airton G. Salles Jr.  ; Sylvio Barbon Junior
; Sylvio Barbon Junior  ; Juliano A. Bonacin
; Juliano A. Bonacin

Prediction of glycerol electrooxidation potentials using machine learning, with improved feature treatment.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250090
J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20250098, 1-7
Ant Colony Optimization for Density Functionals in Strongly Correlated Systems
Gabriel M. Tonin  ; Tatiana Pauletti
; Tatiana Pauletti  ; Ramiro M. dos Santos
; Ramiro M. dos Santos  ; Vivian V. França
; Vivian V. França

Ant Colony Optimization method (inspired by the collective behavior of ants in optimizing paths) to optimize one (1D) to five (5D) parameters of an analytical density functional for the ground-state energy of strongly correlated systems. The performance is assessed by the mean relative error (MRE): for 3D and 5D we find MRE ca. 0.8%, an error reduction of 67% compared to the original parametrization (MRE = 2.4%).
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20250098
Short Report J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36(8), e-20240203, 1-7
Effect of the Alkyl Side Chain of Antitrypanosomal Cinnamate, p-Coumarate, and Ferulate n-Alkyl Esters Using Multivariate Analysis and Computer-Aided Drug Design
Matheus L. Silva; João L. Baldim; Thais A. Costa-Silva; Maiara Amaral; Maiara M. Romanelli; Erica V. C. Levatti; Andre G. Tempone; João Henrique G. Lago

Machine learning and multivariate statistical analyses identified molecular features correlated with biological activity of phenylpropanoid against Trypanosoma cruzi.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20240203
Online version ISSN 1678-4790 Printed version ISSN 0103-5053
Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society
JBCS Editorial and Publishing Office
University of Campinas - UNICAMP
13083-970 Campinas-SP, Brazil
Free access










